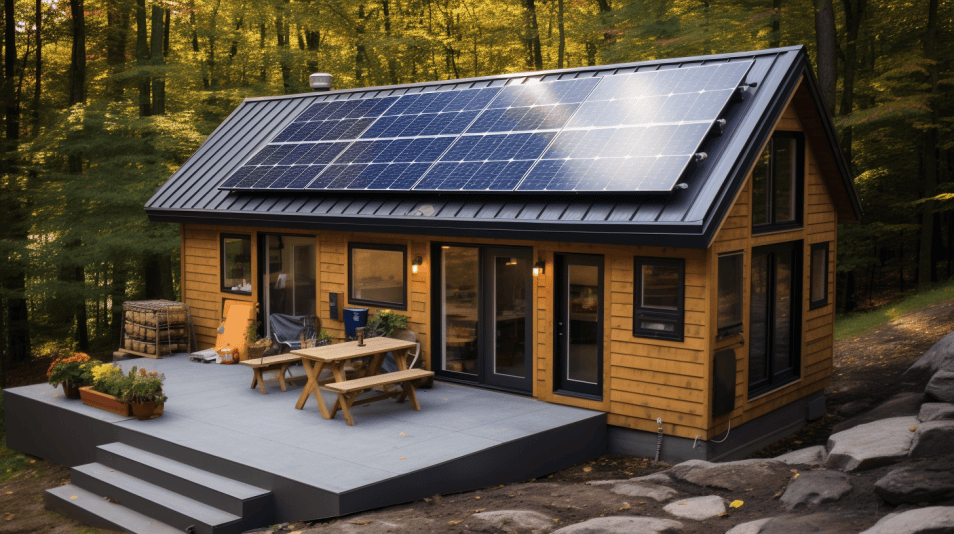
Off Grid Projects
Off-grid living is an increasingly popular lifestyle choice for those who seek independence from the modern world’s conveniences and its dependence on fossil fuels. By leveraging renewable energy sources and carefully managing resources, individuals and families can successfully unplug from the grid and create sustainable, self-sufficient living spaces. From DIY solar panels to water collection systems, off-grid projects embrace a diverse range of skills and technologies.
Understanding the fundamentals of off-grid projects is key to successfully embracing this lifestyle choice. It requires a thorough analysis of energy requirements, water management, food storage, and more. However, with patience, commitment, and resourcefulness, anyone can take the leap towards off-grid living and experience the benefits it offers, such as lower environmental impact and a more self-sufficient way of life.
Key Takeaways
- Off-grid living requires careful planning and resource management
- Renewable energy, water systems, and food preservation are essential aspects of off-grid projects
- Patience, commitment, and resourcefulness are necessary for a successful off-grid lifestyle
Understanding Off-Grid Projects
Off-grid projects are endeavors aimed at achieving a self-sufficient lifestyle by meeting basic needs such as energy, water, and food without relying on public utilities or centralized infrastructure. As someone who appreciates the off-grid lifestyle, I can relate to the desire for independence and sustainable living.
The concept of off-grid living often involves the use of stand-alone systems that harness renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines. Additionally, off-grid systems can include water collection, filtering, and storage, as well as waste management methods like composting toilets. Living in a remote area, where centralized utilities are inaccessible or unreliable, can make off-grid projects a necessity.
For those who aim to adopt an off-grid lifestyle in a remote location, it is essential to plan for a complete system that can accommodate various basic needs. Off-grid systems not only reduce dependency on external resources but often present energy savings techniques that can result in lower monthly expenses.
However, one significant problem that may arise in off-grid living is the lack of access to certain services and resources often taken for granted in urban environments. This challenge, however, can be mitigated by adopting innovative solutions, learning from others’ experiences, and continually improving your off-grid setup.
To embark on off-grid projects, it is crucial to be knowledgeable about the different options available for generating power, storing and managing energy, providing water supply, and addressing waste disposal. Off-grid homes also tend to embrace sustainable design principles, using environmentally friendly and locally sourced materials.
In pursuit of this lifestyle, I have gained a wealth of knowledge about off-grid systems, the various components needed to create an efficient off-grid home, and the challenges that come with adapting to an off-grid way of life. Learning from others and expanding your own knowledge base is critical for effectively implementing off-grid projects and transitioning to an off-grid lifestyle.
Solar Power in Off Grid Projects
As someone passionate about off-grid projects, I’ve found that solar power plays a crucial role in providing a sustainable and efficient source of energy. In this section, I will discuss solar panels and systems, solar energy as a renewable resource, and how to embark on a DIY solar project.
Solar Panels and Systems
Solar panels, made of numerous solar cells, are the foundation of any off-grid solar power system. These panels convert sunlight into electricity that can be used or stored. Off-grid solar systems typically require an array of solar panels, a charge controller, batteries for energy storage, and an inverter to convert the electricity to a usable form. For example, the Family Handyman provides a helpful guide on how to install an off-grid solar power system.
- Solar Cells: The building blocks of solar panels, made from silicon and responsible for converting sunlight into electricity.
- Solar Array: A group of interconnected solar panels that collect sunlight and generate electricity.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the voltage and current from the solar array to protect the batteries from damage.
- Batteries: Store the electricity generated by the solar array for use when the sun is not shining.
- Inverter: Converts the electricity generated by the solar array and stored in the batteries into a form suitable for household appliances.
Solar Energy As a Renewable Resource
Solar energy is an exceptional renewable resource, using the sun’s power to generate electricity without depleting natural resources. It’s an environmentally-friendly option that reduces carbon emissions, helping to combat climate change. Furthermore, off-grid solar electricity is crucial to achieving universal electricity access, with initiatives like the World Bank’s Lighting Global aiming to provide sustainable solar solutions to those living without electricity.
DIY Solar Project
Embarking on a DIY solar project can be a rewarding experience, allowing you to customize your off-grid solar system and save money in the process. A step-by-step guide to building an off-grid solar power system can be helpful in guiding you through the process.
- Plan: Determine how much power you need and create a solar power system design to meet those needs.
- Choose Components: Select the solar panels, charge controller, batteries, and inverter that matches your system requirements.
- Install Solar Panels: Mount the solar panels on your chosen location to maximize sunlight exposure.
- Connect Components: Safely fix and connect the DC cables, install the solar charge controller or off-grid inverter, and properly install the AC and DC breakers.
- Battery Installation: Install the battery in a safe manner, ensuring reliable energy storage.
- Test & Commission: Test the system to ensure everything is working correctly, and make any necessary adjustments.
Undertaking a DIY off-grid solar project can be an exciting and rewarding experience, providing you with a renewable and sustainable source of energy tailored to your specific needs.
Other Energy Sources for Off-Grid Living
As someone who has always been interested in off-grid living, I’ve explored various energy sources to help reduce dependence on traditional electricity. In this section, I’ll discuss wood stoves and heating, as well as wind turbines as alternative power sources for off-grid living.
Wood Stoves and Heating
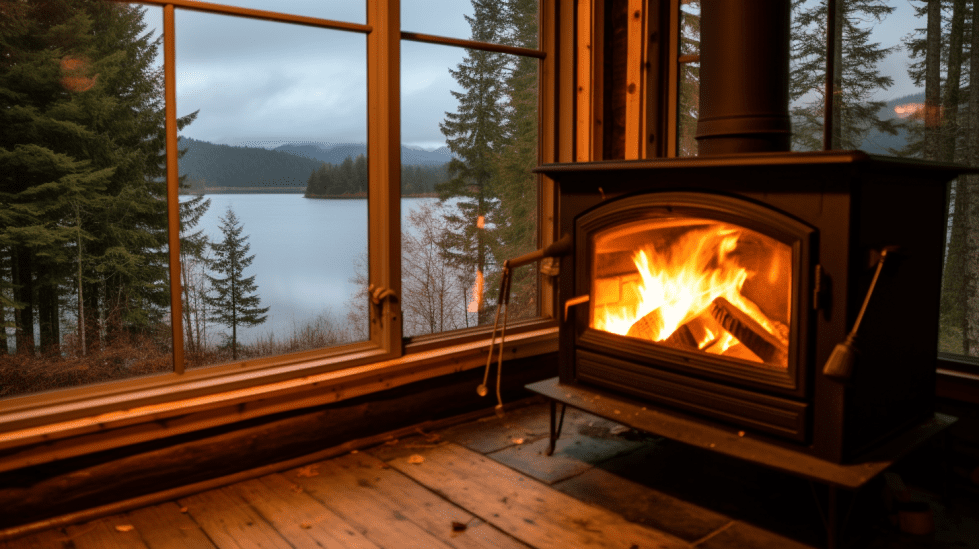

When I first began researching off-grid heating options, I found that wood stoves were a popular choice. A wood stove is an energy-efficient way to heat a home with a renewable resource. Many people who live off the grid appreciate the self-sufficiency and independence that comes with using wood for fuel.
I have seen a few different types of wood stoves, but one that caught my attention is the rocket stove. This type of stove is designed with a unique combustion chamber that allows for efficient burning of small pieces of wood. The chamber directs heat up a chimney-like structure, which in turn distributes the heat as needed. Rocket stoves not only save on fuel consumption but also produce less smoke and particulate emissions compared to traditional wood stoves.
Another key aspect of using wood stoves for off-grid living is the construction of a wooden frame around the stove, which can provide added insulation and help to distribute heat more evenly around the room.
Wind Turbines and Power
Another alternative energy source I’ve considered for my off-grid living project is wind power. This option involves installing a wind turbine on your property to harness the kinetic energy of the wind and convert it into electricity. Wind turbines are a clean and renewable source of energy that can provide power to off-grid homes, particularly in locations with consistent winds.
When looking into wind turbines, I focused on min wind turbines since they are ideal for small-scale, off-grid applications. These turbines are typically more affordable, easier to install, and require less maintenance than their larger counterparts. Additionally, they can be combined with other renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to create a more reliable and diversified off-grid power system.
In conclusion, wood stoves and wind turbines are just a few of the alternative energy sources available for off-grid living. By pairing these options with other renewable technologies, it’s possible to create a sustainable and efficient power system that reduces dependence on traditional electricity sources.
Water Management in Off-Grid Living
Rainwater Collection System
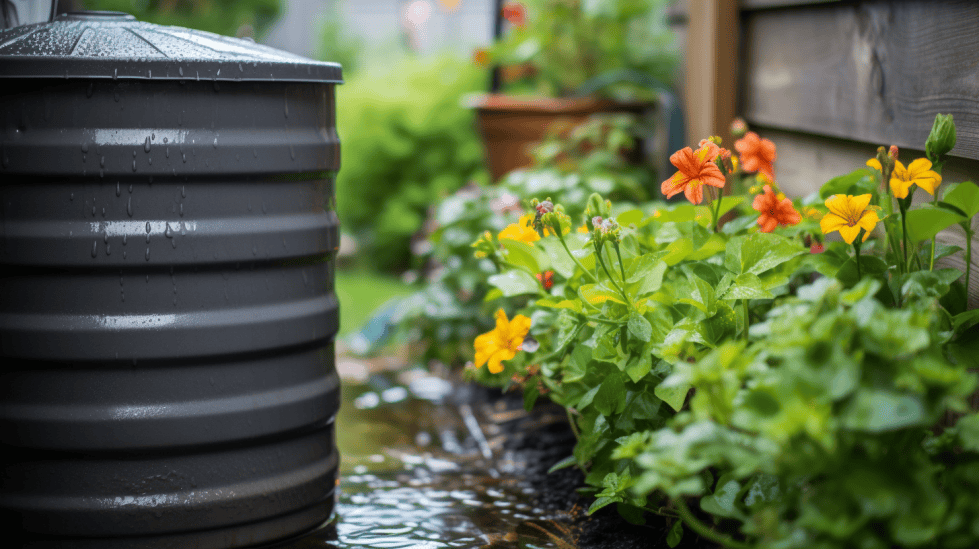

In my off-grid living journey, one of the first steps I took was setting up a rainwater collection system to obtain a reliable and clean water source. Installing rain barrels or cisterns helped me collect and store water efficiently. To maximize my water collection, I placed them in areas that receive consistent rainfall. For ensuring the water I collect is clean, I use a filtration system, such as a water filter, to remove contaminants and purify the water for daily use.
Water Pumping and Heating
To supply my off-grid home with running water consistently, I invested in a water pump that moves water from the collection system to the required destinations like my kitchen and bathroom. For hot water, I use a solar or propane water heater, which provides me with a sustainable and efficient option, without relying on the traditional power grid. Monitoring my water consumption helps me make necessary adjustments and identify areas where I can conserve water.
Sewer and Septic Systems
Managing wastewater is equally important in my off-grid lifestyle. I chose a sewer system or a septic system based on the local, regulatory requirements and environmental factors. A greywater system is used in my off-grid home to divert water that has already been used from the laundry, shower, and sink to other purposes like watering my garden or landscaping, instead of flushing it down the sewer system. This way, I can reuse water and minimize my water waste, contributing to a sustainable and efficient off-grid life.
Living Spaces for Off-Grid Living
Small Houses and Spaces
When it comes to off-grid living, I recommend considering small houses and spaces for a more sustainable lifestyle. Shipping container homes and tiny houses provide an excellent alternative to traditional homes because they utilize limited resources, conserve energy, and can easily be adapted to off-grid living.
Efficiency is crucial in small spaces, so be mindful of appliances such as clothes washers and air conditioners. Opt for energy-saving models or consider alternatives like hand washing or utilizing natural ventilation instead of air conditioning.
Creating Comfortable Spaces
Living off the grid doesn’t mean sacrificing comfort. To create a comfortable space, I suggest considering built-in furniture and sliding doors, which are excellent for maximizing space in small houses. Moreover, efficient energy management can also enhance comfort. For instance, an eco-friendly wood-constructed cabin like Heva in France is designed specifically for off-grid living and offers practical living features within its 22-square meter area.
A crucial factor in off-grid living is a clean and reliable water supply. I recommend investing in a water filtration system, as it ensures potable water suitable for consumption.
In addition, consider a composting toilet which can process human waste into safe and usable compost without requiring a connection to a sewage system. This environmentally-friendly solution can be an excellent addition to your off-grid home.
In conclusion, small houses and spaces, as well as creating comfortable spaces, are essential in off-grid living. Prioritizing efficiency, sustainability, and practical solutions will make your off-grid experience enjoyable and fulfilling.
Food Storage and Preservation
Root Cellars
In my experience, root cellars are an efficient and reliable way to store root vegetables, such as potatoes, carrots, and beets, for extended periods. They take advantage of the earth’s stable temperatures to maintain a cool, dark environment. To create a root cellar, I’ve found that digging a pit or constructing an insulated space below ground level works best. Proper air circulation and humidity control are essential to prevent spoilage and promote longevity. Some key benefits of root cellars include:
- Low energy consumption: Since they don’t require electricity, root cellars are an eco-friendly option for off-grid living.
- Long-term storage: When properly managed, root cellars can preserve food for several months.
Dutch Ovens and Cooking
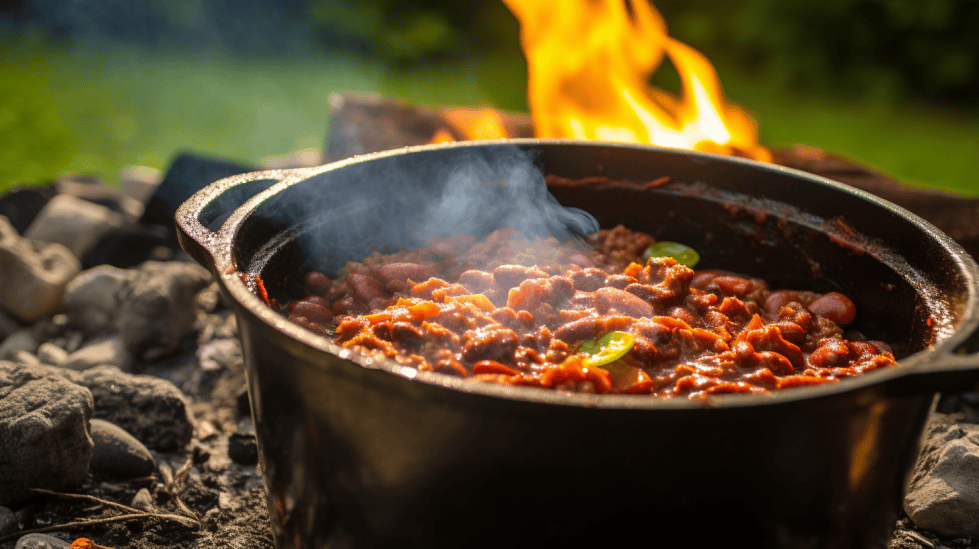

I’ve discovered that Dutch ovens are versatile and practical cooking tools for off-grid living. They are typically made of cast iron or enamel-coated cast iron, making them highly heat-retentive and ideal for slow cooking. From baking bread to simmering stews, I have used Dutch ovens on various heat sources, including open fires, wood stoves, and gas burners.
One key benefit of Dutch ovens is their ability to serve as both a cooking pot and an oven. This versatility means you can prepare a wide range of dishes using just one piece of cookware. Some of the aspects I appreciate about Dutch ovens are:
- Energy efficiency: Their excellent heat retention reduces the need for constant heat input, conserving energy.
- Durability: With proper care, Dutch ovens can last for many generations, making them a valuable investment for off-grid living.
To summarize the section on Food Storage and Preservation, I’ve found that root cellars and Dutch ovens provide practical, energy-efficient, and sustainable options to store and cook food in off-grid environments. By utilizing these methods, you can maintain a nutritious and diverse diet while living in harmony with nature.
Cost and Economic Impact of Off Grid Living
In recent years, I’ve gained an interest in off-grid living and have researched its costs and economic impact. One of the most apparent benefits of living off the grid is the reduction in utility bills, which would have a positive effect on my long-term cost of living. Installing solar panels, digging a well, or buying a wood stove represent some of the initial investments required to set up an off-grid lifestyle. However, these initial expenses are expected to be outweighed by the long-term savings.
As someone who constantly seeks innovative ways to live sustainably, I find that off-grid living can also contribute positively to economic growth. By investing in alternative energy sources such as solar or wind and promoting local businesses, a shift towards a more sustainable economy is supported. In fact, I’ve learned that in some cases, off-grid renewable power systems, like solar/wind/hydrogen storage, can be cheaper than extending the grid to remote communities.
Furthermore, the off-grid lifestyle can lead to various socio-economic benefits. For instance, a study on rural electrification showed that off-grid systems led to improvements in income due to increased non-agricultural activities. This positive impact is an additional incentive for me to transition towards such a lifestyle.
In terms of personal finances, the cost of living off the grid might seem high at first glance. For example, acquiring land, constructing an eco-friendly shelter, and setting up water, energy, and waste disposal systems can entail a considerable amount of money. However, I believe that the long-term advantages, such as the reduction in utility bills and increased self-sufficiency, make the investment worthwhile.
Overall, my research has led me to conclude that the cost and economic impact of off-grid living have both positive and challenging aspects. Nevertheless, the potential benefits it offers to both my personal finances and the broader economy make it an appealing option to explore further.
Off Grid Living in Different Regions
As someone who is passionate about off-grid living, I have observed various approaches to off-grid projects in different regions. In this section, I will discuss off-grid projects in North America, Sub-Saharan Africa, and South Africa. I will focus on the unique challenges and opportunities these regions present for off-grid living.
Off Grid Projects in North America
In North America, off-grid living is often associated with a desire for self-sufficiency and a sustainable lifestyle. Many off-grid projects in this region focus on harnessing renewable energy, like solar panels and wind turbines. In rural areas, off-grid residents might also rely on wood stoves for heating and propane or natural gas for other energy needs.
Some popular off-grid projects in North America include rainwater harvesting, gardening, and food preservation techniques, such as canning and dehydration. There are also numerous off-grid communities that provide an opportunity for like-minded individuals to collaborate on shared resources and skill-building.
Off Grid Projects in Sub-Saharan Africa
In Sub-Saharan Africa, off-grid living is more about energy access than it is about sustainability. In many parts of the African continent, access to reliable electricity is a significant challenge. To address this issue, organizations like Power Africa promote off-grid solutions as a way to increase energy access for millions of people.
Solar projects are particularly popular in this region, providing clean and affordable energy to remote and underserved communities. Additionally, off-grid living in Sub-Saharan Africa often includes projects like water purification systems, improved cookstoves, and biogas digesters that transform waste into energy. These solutions aim to mitigate the effects of energy poverty and positively impact the lives of people living in rural and urban households.
Off Grid Projects in South Africa
South Africa offers an interesting contrast to the rest of the African continent when it comes to off-grid living. While the country faces similar challenges regarding energy access, it has experienced a rise in interest in off-grid living for sustainable and independent reasons, similar to North America.
In South Africa, off-grid projects often revolve around solar energy systems, water conservation and harvesting, and permaculture or organic gardening. Networks like the South African Off-Grid Living Network and the Sustainable Energy Society of Southern Africa provide resources and opportunities for collaboration.
In conclusion, each region brings unique challenges and opportunities to off-grid living projects. By exploring how communities in these regions approach off-grid living, we can learn valuable insights and adapt strategies for sustainable, independent, and equitable energy access worldwide.
Potential Challenges and Solutions in Off Grid Living
As someone who has ventured into off-grid living, I encountered a few challenges. One of the primary obstacles in off-grid living is maintaining a reliable electricity source. Fortunately, there are solutions available such as investing in solar panels, wind turbines, or even a backup generator. To optimize power usage, I recommend considering energy-efficient appliances and minimizing the reliance on electronic devices (Off Grid Homesteading).
Another challenge I faced was the distance from the electricity grid, which made it essential for me to become more self-reliant. By employing sustainable solutions like rainwater collection, composting toilets, and growing one’s own food, I managed to minimize my dependency on external resources.
Power outages can be a concern for those living off the grid, but there are ways to approach this situation. For example, I installed a robust battery storage system for my solar panels, ensuring that electricity is available even during periods of low sunlight. It is also a good idea to have backup power options like a generator or propane heaters for colder months.
Living off the grid can sometimes feel like a survival situation, especially during emergencies. To tackle this, I have prepared a well-stocked emergency kit with essential supplies like food, water, and first aid items. Planning ahead by learning essential survival skills can also prove invaluable in such circumstances.
Lastly, one of the most significant challenges I faced when starting out was the lack of technical assistance. In order to overcome this, I connected with online forums, local communities, and social media groups dedicated to off-grid living. Additionally, I invested time in learning about various off-grid technologies and foundational skills, such as carpentry and gardening.
By acknowledging these potential challenges and finding suitable solutions, I found that off-grid living can be a vastly rewarding experience (8 Challenges of Off-Grid Living and How to Conquer Them).
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some affordable off-grid energy solutions?
When it comes to affordable off-grid energy solutions, solar panels are often the first choice. Solar panels can be used to generate electricity to power your off-grid project. If you’re disconnected from the power grid, you’ll need an off-grid system with batteries to store the energy for later use. For more information, you can explore grid-tied vs. off-grid solar.
How can I source water for my off-grid project?
Sourcing water for your off-grid project can involve multiple methods. Some options include collecting rainwater, drilling a well, and tapping into nearby streams or springs. It’s crucial to consider local regulations and test water sources for purity before using them for drinking or irrigation.
Which are the essential off-grid survival skills?
Living off-grid often requires essential survival skills to maintain a comfortable and safe lifestyle. These core skills should include:
- Gardening and food production knowledge
- Basic construction and carpentry capabilities
- Animal husbandry and hunting abilities
- Water collection and purification techniques
- Emergency first aid and medical awareness
- Basic fire-making and fire safety measures
- Navigation, signaling, and outdoor safety skills
How do I build an off-grid shelter or cabin?
Building an off-grid shelter or cabin requires planning, preparation, and various construction skills. Choose a suitable location, taking into account factors like sunlight exposure, access to water, and potential hazards. Study local building codes and obtain necessary permits before starting construction. Research different building materials and methods, such as timber, straw bale, and earthbag construction, depending on your budget and design preferences.
What are the best ways to grow food off-grid?
Growing food off-grid requires planning and knowledge of sustainable agriculture practices. Consider the following methods:
- Create a permaculture garden to mimic natural ecosystems and promote biodiversity.
- Use raised beds or containers to maximize space and control soil quality.
- Compost kitchen and yard waste for a natural and cost-effective fertilizer.
- Implement a small-scale aquaponics or hydroponics system for efficient and water-saving food production.
- Practice crop rotation, companion planting, and natural pest control to maintain healthy and productive gardens.
How can I maintain communication while living off-grid?
Maintaining communication while living off-grid can be achieved through various means. A satellite phone enables you to stay connected with emergency services and loved ones, regardless of your location. Ham or shortwave radios also provide long-distance communication capabilities. For internet access, consider a satellite-based service. Be mindful of power sources and have backup power options to ensure consistent communication access.