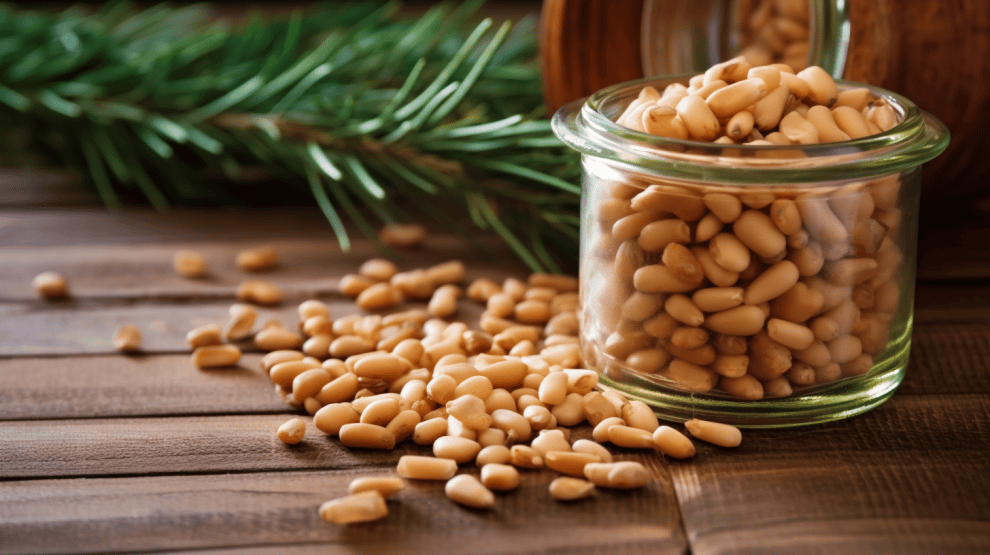
Are All Pine Nuts Edible?
Pine nuts have long been enjoyed for their unique flavor and added crunch in various dishes. These edible seeds come from pine cones and are harvested from certain types of pine trees. They’ve been consumed in Europe and Asia since the Paleolithic period, and today they are a popular addition to meat, fish, salads, and vegetable dishes, as well as being baked into bread. But are all pine nuts edible? That’s a question I’ve been curious about myself.
From my research, I discovered that not all pine trees and cones produce edible seeds. Some species yield the delicious, nutrient-rich seeds we know and love, while others might not be as suitable for consumption. It’s essential to know which pine species contain edible seeds to avoid any potentially harmful effects. I learned that before consuming pine nuts from any pine tree, one should be certain that the species is known to produce edible seeds.
As a lover of pine nuts, I often get asked whether all pine nuts are edible. I’ll dive into the different types of pine nuts and address their edibility in this section.
Types of Pine Nuts
When it comes to pine nuts, it’s important to note that they are actually the edible seeds of pine trees, found inside the hard, inedible casing of pine cones. There are many species of pine trees, but not all of them produce edible seeds. Let me explain further.
- Pignoli: These are the pine nuts that most people are familiar with. They originate from the Mediterranean region and are commonly used in Italian dishes, such as pesto sauce. Pignoli are harvested from the stone pine tree (Pinus pinea). These seeds are indeed edible and nutritious.
- Pinon: Also known as the New Mexico pine nut or Colorado pine nut, these are harvested from the pinon pine tree (Pinus edulis). They are a bit smaller than Pignoli but equally tasty and edible. They’re traditionally used in Native American cuisine and often roasted or used to make pinon coffee.
While there are other species of pine trees which produce seeds, not all of them are considered edible or palatable. It’s essential to be cautious when harvesting pine nuts in the wild. Only consume seeds from known edible species, such as Pignoli or Pinon, and avoid consuming pine nuts from unknown species of pine trees.
In conclusion, while many pine nuts are indeed edible, not all of them are. Stick to the familiar types, such as Pignoli and Pinon, for safe and delicious consumption!
Culinary Uses and Nutritional Benefits
Recipes and Dishes
Pine nuts have a variety of uses in the kitchen, and I often find them to be versatile, delicious, and nutritious ingredients. One of my favorite ways to use pine nuts is in pesto sauce, where they blend perfectly with fresh basil, Parmesan cheese, and olive oil. I also enjoy adding them to my salads for a boost of flavor and nutrition.
When I’m in the mood for something sweet, I bake pignoli cookies or sprinkle pine nuts onto my favorite desserts. These nuts add a delightful crunch and an appealing taste to any dish. Another way I like to incorporate pine nuts into a meal is by blending them into hummus for a unique and appetizing twist.
Nutritional Content
I find that pine nuts are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients. They are an excellent source of protein and fiber, which can help with weight management and heart health. Pine nuts also contain significant amounts of vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that supports the immune system and skin health.
Moreover, pine nuts are rich in:
- Magnesium, which can aid in maintaining a healthy heart and strong bones
- Zinc, which helps in immune system function and wound healing
- Iron, necessary for oxygen transportation and energy production
- Manganese, important for bone health and metabolism.
The nutritional profile of pine nuts includes:
- Calories: 191
- Fat: 19g
- Sodium: 0.6mg
- Carbohydrates: 3.7g
- Fiber: 1.1g
- Sugars: 1g
- Protein: 3.9g
- Magnesium: 71mg
- Zinc: 1.8mg
- Iron: 1.6mg
- Manganese: 2.5mg
- Vitamin E: 2.6mg
- Vitamin K: 15.3mcg (source)
In addition, pine nuts contain omega-3 fatty acids and unsaturated fats, which are both essential for heart health and overall well-being. Pine nut oil, derived from these nuts, has its own medicinal properties and can be used as a salad dressing or drizzle on dishes for added flavor and nutritional benefits.
I find that including pine nuts in my diet allows me to enjoy tasty recipes while also contributing to a balanced and nutritious meal plan.
Pine Nuts Harvesting and Processing
Harvesting Methods
When it comes to harvesting pine nuts, I found that it’s essential to be patient and methodical. Typically, pine nuts are found inside pine cones, so the first step in the harvesting process is collecting mature pine cones. I usually use a long, thin pole to gently shake the higher branches of a pine tree and harvest the cones that fall.
To prevent the small seeds from spilling out and to protect my hands, I place a large burlap bag underneath the tree to catch the falling cones. The best time to harvest pine cones is in late summer or early fall, when they’re still on the tree but haven’t fully opened yet.
Drying and Processing
After collecting the pine cones, I transfer them to a well-ventilated, shady, and dry area, laying them out in a single layer to allow for proper drying. This process may take a few weeks, depending on weather conditions. As the cones dry, they gradually open, revealing the seeds.
Once the pine cones are fully opened, I gently shake or tap each one to release the pine nuts. The seeds are still enclosed in a hard, outer shell, so I proceed with cracking the shell to extract the edible part. This requires a bit of force, but it’s essential to be cautious because the inner seed is delicate.
The final step is the removal of the second shell that surrounds the actual pine nut. It is thinner, with a papery appearance, and can be easily peeled off. This step will ultimately expose the edible part of the pine nut, which can be eaten straight away or used in various recipes.
During this entire process, I make sure to handle the pine nuts gently and keep them free from contaminants, ensuring their quality and safety for consumption. While pine nuts can be enjoyed in their natural state, they can also be utilized in other forms, such as pine nut tea, high in EPA, which is beneficial for overall health and well-being.
Pine Nut Syndrome and Health Concerns
Pine Nut Syndrome
I’ve come across a peculiar condition called Pine Nut Syndrome or pine mouth, which can affect some people after consuming pine nuts. This syndrome causes a bitter or metallic taste that can last from a few days up to 2 weeks. It usually develops 12 to 48 hours after eating pine nuts and can hinder one’s enjoyment of food and drink during this time. It’s important to note that not everyone experiences pine nut syndrome, and it doesn’t cause any lasting harm.
Preventing and Addressing Health Concerns
While pine nut syndrome is a concern, I’d like to highlight some of the health benefits of pine nuts. They are rich in nutrients such as magnesium, iron, antioxidants, zinc, and protein. These nutrients can help with various health issues like:
- Heart Health: Pine nuts can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase HDL (good) cholesterol. This may lower the risk of heart disease.
- Brain Health: Antioxidants present in pine nuts can help protect brain cells and fight against dementia and other age-related cognitive decline.
- Type 2 Diabetes: The manganese and protein in pine nuts can assist in stabilizing blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes.
Whether pine nuts are consumed raw or roasted, they provide these health benefits. However, pine nuts also contain copper, which can lead to potential health issues like liver complications and scurvy if consumed in excessive amounts.
To prevent such health concerns, it’s essential to consume pine nuts in moderation and maintain a balanced diet. Additionally, to avoid pine nut syndrome, I suggest being cautious about the origin and freshness of the pine nuts being purchased and consumed – opting for high-quality, fresh pine nuts whenever possible.
By staying mindful of the potential risks while enjoying pine nuts, I can appreciate their nutritional benefits and their unique flavor in various dishes, such as traditional Italian pesto sauce and pignoli cookies.
Varieties and Regions
When it comes to pine nuts, not all of them are edible. Among the various species of pine trees, only a select few produce nuts that can be consumed. I found that the primary pine nut producing species include pinyon (or pinon) pines in North America, Italian stone pine in Europe, and Chinese nut pine in Asia.
In North America, the pinyon pines, such as the Mexican pinon and Colorado pinion, thrive in the warmer southwestern regions. These trees have unique characteristics such as gray-colored bark, short needles, and round-shaped cones. The nuts produced by pinyon pines have a distinct buttery flavor, making them great additions to various dishes.
Europe is home to the Italian stone pine, which produces a popular variety of pine nuts known for their unique elongated shape. These can be mainly found in the Mediterranean regions, where they have been consumed since ancient times. Their smooth texture and mildly sweet taste make them a favorite ingredient in several European cuisines.
Moving on to Asia, the Chinese nut pine produces edible pine nuts as well. Like other varieties, these nuts have a subtle and delicate flavor, with each nut encased in a hard shell. These trees can be easily identified by their long needles and thick bark, which protect them in colder climates.
Not only are pine nuts delicious, but they also provide various health benefits, primarily due to their rich nutrient content. I discovered that these nuts contain essential minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which contribute to bone health. Some pine species also produce pine pollen, known for its potential health benefits when consumed in moderation.
In summary, while not all pine trees produce edible nuts, the ones that do offer distinct flavors and health benefits, depending on the variety and region. With this information about pine nuts, I hope that you can better appreciate the diversity and characteristics of these nutritious and versatile seeds.
Environmental and Sustainable Impact
As someone who cares about the environment, it’s important to know the sustainability aspect of the various edible parts of pine trees. Pine nuts, for example, are the edible seeds produced by only a few pine species across the globe. While all pine trees produce seeds, only some of them yield edible seeds.
When it comes to sustainability, the main environmental concern for harvesting pine nuts is their extraction from the trees. However, their production is limited to a small percentage of the world’s tree nut crop, primarily by Chinese companies. This implies a relatively high carbon footprint when considering the shipping of these nuts.
The good news is that pine nuts appear to be more sustainable than some other nuts since they don’t cause significant harm to land, soil, air, and water if harvested without pesticides. They share ethical concerns with other nuts, though, like the exploitation and low pay of workers. Thus, it’s essential to choose sustainably sourced pine nuts whenever possible.
Pine trees are conifers that provide other edible parts and products with less environmental impact than the nuts, such as resin, pine tea, pine needle soda, pine bark, and more. For instance, I can easily harvest and utilize the inner bark of white pines, which is rich in nutrients and makes for a delicious and sustainable food source.
Some edible plants that grow alongside pine trees, such as slippery elm, are full of tannins and can offer additional sources of nutrition. These tannin-rich plants can often be found in sustainable forests, which is a great way to incorporate more ecological resources into our daily life.
In conclusion, incorporating pine nuts and other products from pine trees can be a sustainable choice when we ensure ethical sourcing and minimal ecological impact. By exploring other edible parts of the pine tree and their neighboring plant species, I am confident in my ability to make eco-conscious decisions about sourcing and consuming these forest-derived foods.
Price and Market Factors
In my research, I’ve found that the price of pine nuts can be influenced by several factors. Firstly, the volume and prices of pine nuts can be affected by weekly marketing and supply chain conditions, which in turn are influenced by factors like pests, weather, imports, exports, retail promotions, and labor disruptions (USDA ERS).
Another reason for the fluctuation in prices is the varying supply and demand. It is known that poor crops, increased demand, and climate change all play a role in the pricing of pine nuts (The Seattle Times). For instance, when there is a poor harvest of pine nuts due to unfavorable weather conditions, the prices typically increase due to a decrease in supply.
It is also important to note that not all pine nuts are the same, as the most commonly harvested seeds come from four particular pine tree varieties, including the Mexican pinon, the Colorado pinion, the Italian stone pine, and the Chinese nut pine (The Spruce Eats). The prices for pine nuts from different species may vary based on factors like flavor, size, and regional availability.
Lastly, the process of harvesting pine nuts can be time and labor-intensive, which contributes to their higher price tag. Pine nuts need to be collected, shelled, and processed before they reach the market, making them more expensive than other nuts with less involved harvesting processes (PDF – Pine Nuts).
To sum up, the price and market factors affecting pine nuts include:
- Weekly marketing and supply chain conditions
- Supply and demand influenced by factors like pests, weather, and climate change
- Varieties of pine nut species
- Time and labor-intensive harvesting processes
Conclusion
In my research, I discovered that while not all pine nuts are created equal, they are indeed edible. Pine nuts actually come from the seeds of various species of pine trees, and can be found in a protective encasement within the pine cones. Although the seeds of all pine trees can be consumed, there are approximately 20 species with large edible pine nuts, which are mostly found in warm-climate areas.
I also learned how versatile pine nuts can be when it comes to their culinary uses. They can be eaten raw, roasted, added to salads, sprinkled on hummus, or even used in sauces like pesto. Pine nuts’ unique flavor profile makes them a favorite in many dishes, especially Italian cuisine.
When it comes to their nutritional benefits, I found that pine nuts are a healthy choice. They are packed with vitamins and minerals, and even contain heart-healthy fats. However, it’s important to consume them in moderation due to their high calorie content.
In conclusion, I found that not only are pine nuts edible, but they also offer significant health benefits and culinary versatility. So next time you come across these tiny seeds, don’t hesitate to incorporate them into your diet and enjoy their unique taste and nutritional advantages.